Speeding Up Redshift Queries
Waiting minutes and minutes, maybe even an hour, for your queries to compute is an unfortunate reality for growing companies. Whether your data has grown faster than your cluster, or you’re running too many jobs in parallel, there are lots of reasons your queries might be slowing down.
To help you improve your query performance, this guide takes you through common issues and how to mitigate them.
Common Causes for Slow Queries
1. Not enough space
As your data volume grows and your team writes more queries, you might be running out of space in your cluster.
To check if you’re getting close to your max, run this query. It will tell you the percentage of storage used in your cluster. Segment recommends that you don’t exceed 75-80% of your storage capacity. If you approach that limit, consider adding more nodes to your cluster.
SELECT sum(pct_used);
FROM svv_table_info;
Learn how to resize your cluster.
2. Inefficient queries
Another thing you’ll want to check is if your queries are efficient. For example, if you’re scanning an entire dataset with a query, you’re probably not making the best use of your compute resources.
Some tips for writing performant queries:
-
Consider using
INNER joinsas they are more efficient thanLEFT joins. -
Stay away from
UNIONwhenever possible. -
Specify multiple levels of conditionals when you can.
-
Use
EXPLAINto show the query execution plan and cost.
To learn more about writing beautiful SQL, check out these resources:
3. Running multiple ETL processes and queries
Some databases like Redshift have limited computing resources. Running multiple queries or ETL processes that insert data into your warehouse at the same time will compete for compute power.
If you have multiple ETL processes loading into your warehouse at the same time, especially when analysts are also trying to run queries, everything will slow down. Try to schedule them at different times and when your cluster is least active.
If you’re a Segment Business Tier customer, you can schedule your sync times under Warehouses Settings.
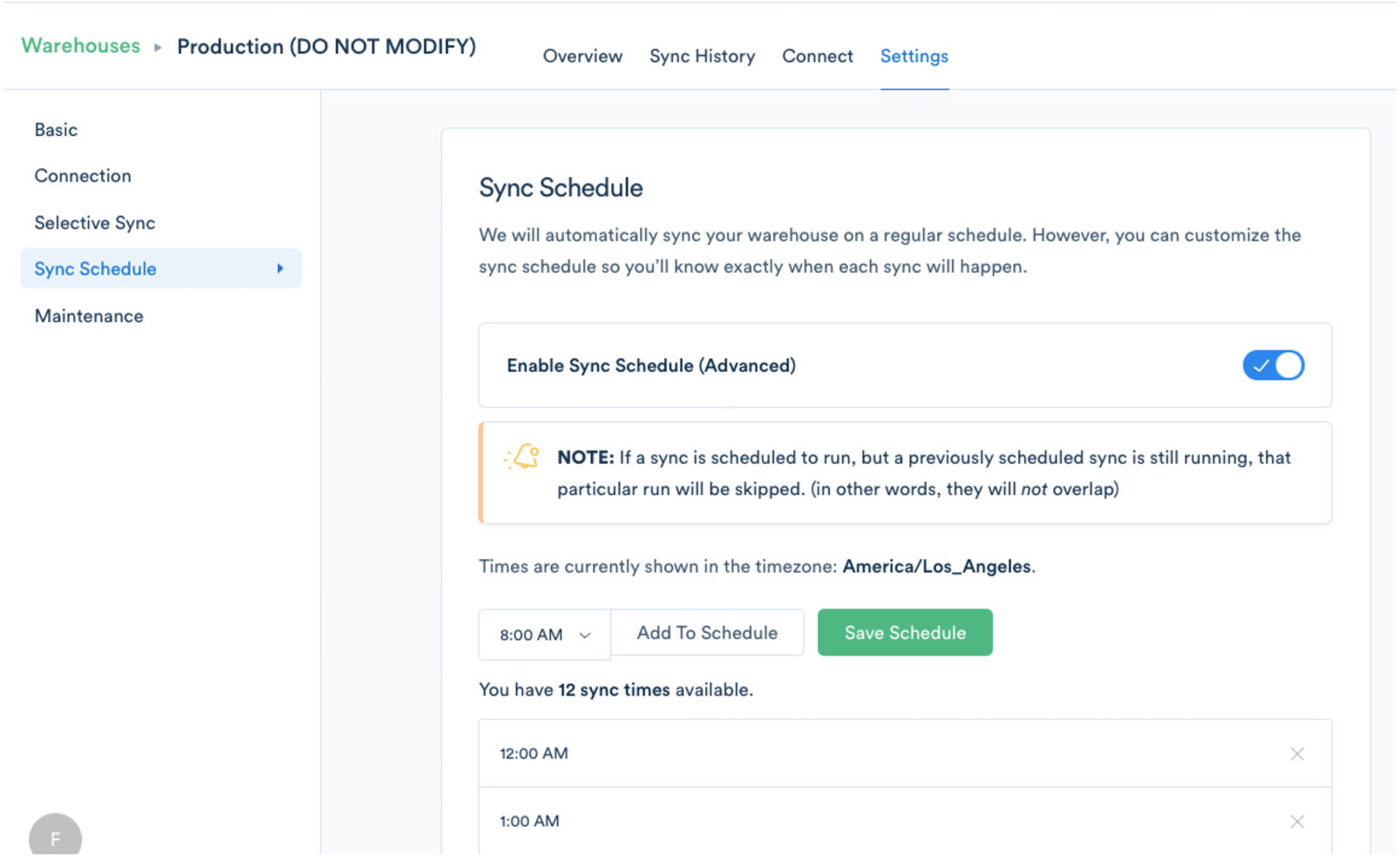
You also might want to take advantage of Redshift’s Workload Management that helps ensure fast-running queries won’t get stuck behind long ones.
4. Default WLM Queue Configuration
As mentioned before, Redshift schedules and prioritizes queries using Workload Management. Each queue is configured to distribute resources in ways that can optimize for your use-case.
The default configuration is a single queue with only 5 queries running concurrently, but Segment discovered that the default only works well for low-volume warehouses. More often than not, adjusting this configuration can improve your sync times.
Before Segment’s SQL statements, Segment uses set query_group to "segment"; to group all the queries together. This allows you to create a queue that isolates Segment’s queries from your own. The maximum concurrency that Redshift supports is 50 across all query groups, and resources like memory distribute evenly across all those queries.
Segment’s initial recommendation is for 2 WLM queues:
-
a queue for the
segmentquery group with a concurrency of10 -
leave the default queue with a concurrency of
5
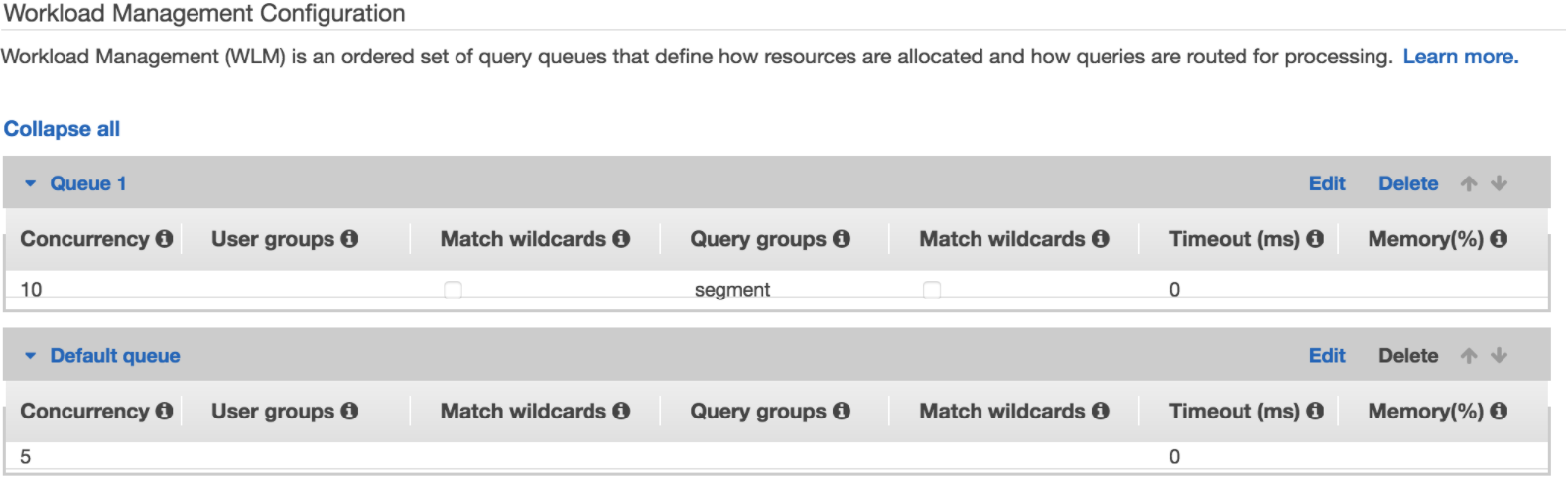
Generally, Segment is responsible for most writes in the databases Segment connects to, so having a higher concurrency allows Segment to write as fast as possible. If you’re also using the same database for your own ETL process, you may want to use the same concurrency for both groups. You may even require additional queues if you have other applications writing to the database.
Each cluster may have different needs, so feel free to stray from this recommendation if another configuration works better for your use-case. AWS provides some guidelines, and you can always contact us as Segment is more than happy to share the learnings while working with Redshift.
Pro-tips for Segment Warehouses
In addition to following performance best practices, here are a some more optimizations to consider if you’re using Segment Warehouses.
Factors that affect load times
When Segment is actively loading data into your data warehouse, Segment is competing for cluster space and storage with any other jobs you might be running. Here are the parameters that influence your load time for Segment Warehouses.
- Volume of data. Segment’s pipeline needs to load and deduplicate data for each sync, so having more volume means these operations will take longer.
- Number of sources. When Segment starts a sync of your data into your warehouse, Segment kicks off a new job for every source you have in Segment. The more sources you have, the longer your load time could take. This is where the WLM queue and the concurrency setting can make a big difference.
- Number and size of columns. Column sizes and the number of columns also affect load time. If you have long property values or lots of properties per event, the load may take longer as well.
Performance optimizations
To make sure you have enough headroom for quick queries while using Segment Warehouses, here are some tips!
- Size up your cluster. If you find your queries are getting slow at key times during the day, add more nodes to give enough room for Segment to load data and for your team to run their queries.
- Disable unused sources. If you’re not actively analyzing data from a source, consider disabling the source for your Warehouse (available for business tier). If you don’t use a source anymore—perhaps you were just playing around with it for testing, you might even want to remove it. This will kick off fewer jobs in Segment’s ETL process.
- Schedule syncs during off times. If you’re concerned about query times and you don’t mind data that’s a little stale, you can schedule your syncs to run when most of your team isn’t actively using the database. (Available for business tier customers.)
Hopefully these steps will help to speed up your workflow! If you need any other help, feel free to contact us.
This page was last modified: 21 Apr 2023
Need support?
Questions? Problems? Need more info? Contact Segment Support for assistance!